B2A/121, Dharam Marg, Landmark: Opp City Union Bank, Near Janakpuri East Metro Station, Delhi - 110058

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) also called sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections that mainly spread through sexual activities such as vaginal anal and oral sex. They can also spread through close skin contact and in some situations from mother to child during pregnancy birth or breastfeeding. Sexually transmitted diseases are caused by different types of germs like bacteria viruses and parasites. If these infections are not diagnosed on time and treated quickly they can lead to several health problems.

The medical term for “pimples” is acne. Acne is the result of changes that occur during puberty. The skin makes oil in sebaceous glands that are found in the deeper layers of the skin. “Whiteheads” or “blackheads” are clogged sebaceous glands. People with acne have glands that make more oil and are more easily plugged, causing the glands to swell. Hormones, bacteria (called P. acnes) and your genetic susceptibility also play a role.

Allergic contact dermatitis is inflamed skin (dermatitis) that occurs when allergy-causing substances (allergens) touch the skin. In people who are sensitive to them, the allergens cause a skin reaction resulting in itching, redness, scaling, and a rash.
Common allergens include metals, rubber, dyes, antibiotics, cosmetics, preservatives, and fragrance.
PPD may be mixed with henna for temporary tattoos. People who are allergic to PPD will react to these tattoos. In bad reactions, scars may result.
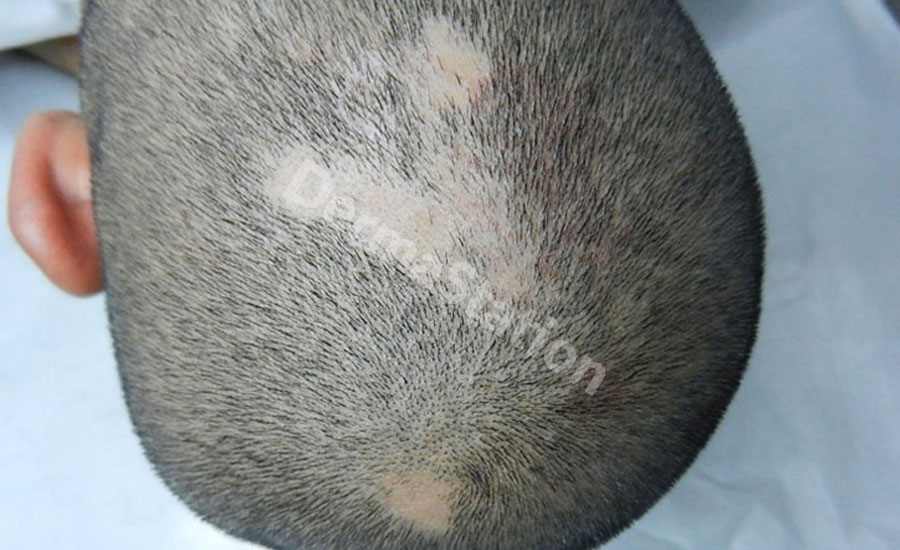
Alopecia means hair loss. Alopecia areata is one of the most common hair loss disorders characterized by loss of hair in well-defined round patches, usually on the scalp. The exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, but it seems to be caused by the immune system attacking the hair follicles by mistake. When the follicle is attacked, this causes the hair to fall out just below the surface of the skin.

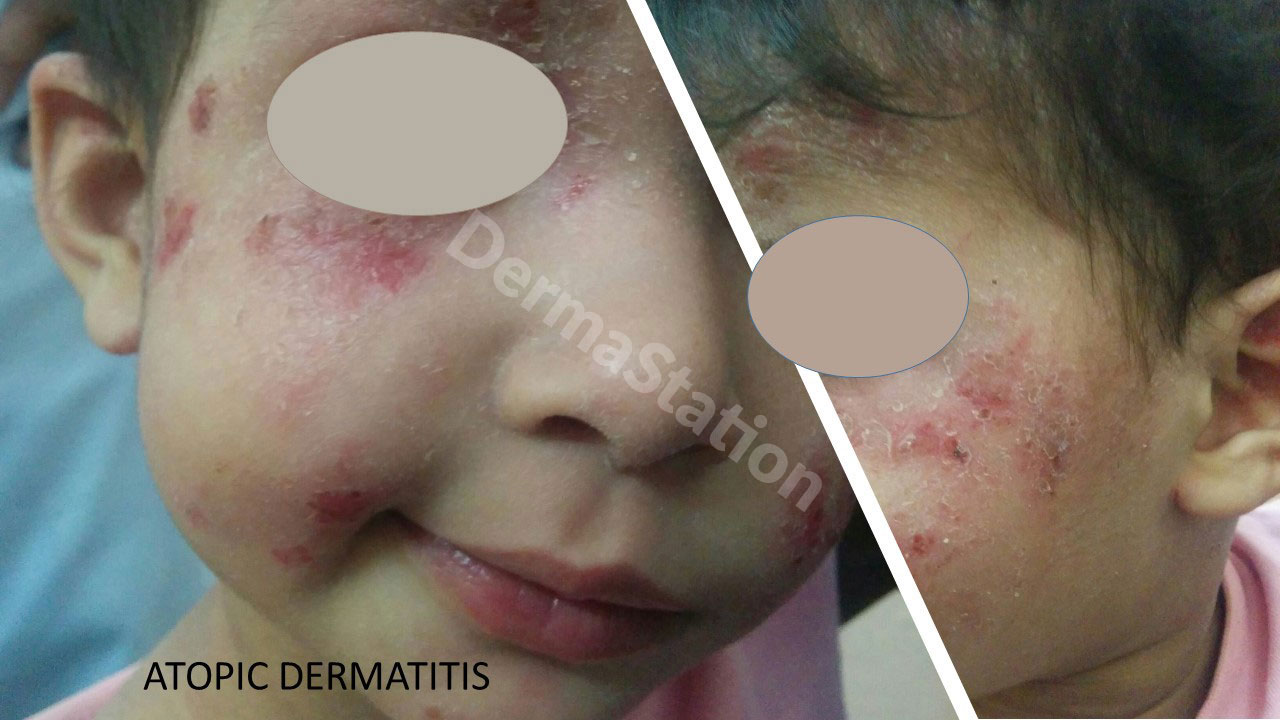
Atopic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition in which the skin appears inflamed, red, itchy and dry. It commonly affects children.
It is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic factors include deficiency in the proteins that form the skin barrier. The skin loses moisture more easily, becoming more dry, easily irritated, and hypersensitive. The skin is also more prone to infection (with bacteria, viruses, or fungi). The immune system overreacts to environmental triggers such as pet dander and dust mites. Allergies and asthma may be present more frequently in individuals with atopic dermatitis.
In infants, atopic dermatitis often starts as a dry red rash on the cheeks and around the mouth, often made worse by drooling. As children grow older, the rash is more common on the arms, legs, and in areas where they are easily able to scratch. In teenagers, eczema is often on the inside the elbows, behind the knees, on the hands and feet, and around the eyes.
Scabies is a common skin problem caused by the human itch mite. People of any age, race and social group can get scabies, regardless of personal hygiene.
The mite is transmitted by close skin-to-skin contact. The mite burrows into the upper layers of skin, where it feeds and lays eggs. After a few weeks, the patient develops an allergic reaction causing the very itchy scabies rash.
The rash can look like hives, pimples, blisters or scaly and crusted bumps. It is common to see the rash on the hands, feet, underarms, belly button and genitals.
It is important to treat all close contacts, not only those who have the rash.
Bullous diseases are a group of rare fluid-filled blistering diseases characterized by formation blisters on the skin and mucous membranes. The blisters rupture to form raw and sore areas.

Types Of Bullous Disease
-
PEMPHIGUS
The blisters in pemphigus are soft, flaccid, and rupture easily.
-
PEMPHIGOID
Pemphigoid causes deep-seated blisters which do not rupture easily.
-
DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS
DH has small blisters, and raw areas of skin with intense itching. People with DH are usually sensitive to gluten, the protein found in wheat, barely, and rye.
-
ACQUIRED EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
In “epidermolysis bullosa acquista,” the blisters form on the hands, knees, elbows, and ankles i.e easily traumatized sites. Scars form on healing which can disfigure hands, nails, and other areas.
There are a variety of common benign (not cancerous) growths that can appear on the skin. Some appear after an injury to the skin or after years of sun damage. Some arise for no reason at all.

Cherry Angioma
A cherry angioma is small bright red or purple growth comprising of many small blood vessels. They can grow anywhere on the body, most often on the trunk. Larger angiomas may bleed and need to be removed.
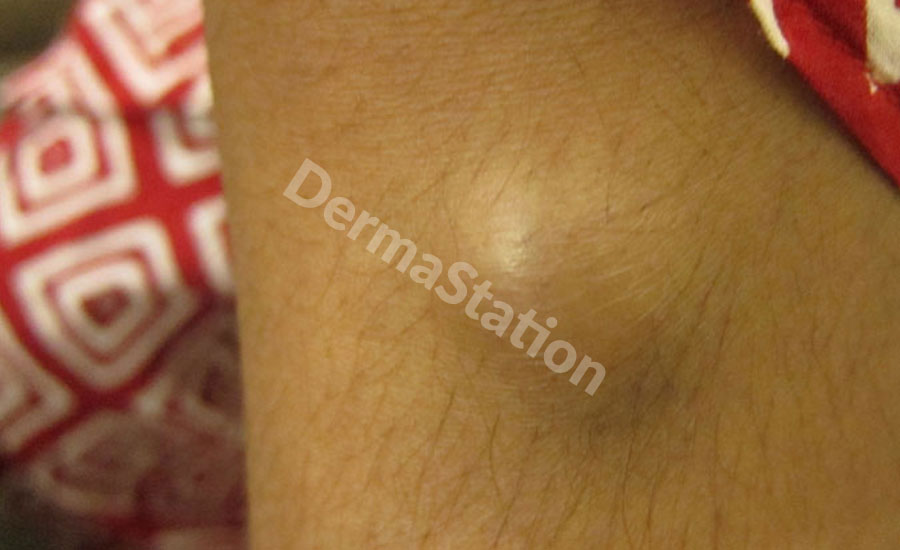
Cysts (Epidermoid and Pilar)
An epidermoid cyst, also called a sebaceous cyst, forms when an oil gland in the skin become plugged. They are most common on the face, neck, and back though they can form on any part of the body. When squeezed, an epidermoid cyst releases a foul-smelling cheesy discharge.
A pilar cyst forms from a hair follicle. They are flesh-colored, dome shaped growths. A cyst that ruptures, becomes inflamed, and causes pain, may look like a boil and usually requires drainage, an antibiotic and possibly removal.
Dermatofibroma
Dermatofibroma are small, pink, dull red or brown growths that appear after a minor skin injury such as an insect bite or acne. They may look like a mole or scar. Dermatofibromas feel firm to touch, and will pucker or dimple when pinched.
Lipoma

A lipoma is a benign tumor made up of fat cells that lies deep in the skin and feels like a soft lump. Lipomas do not require treatment unless they grow extremely large or become painful.
Milia
Milia are a type of epidermoid cyst that appear on the eyelids and cheeks as tiny white bumps. These cysts are common in order women and children.
Moles

Moles are round, flat or slightly raised growths that can appear anywhere on the body. They are often one color-brown, flesh-colored, red, pink, blue, or black. Moles. If a mole is changing color, itching, or bleeding, consult your dermatologist.
Neurofibroma
A Neurofibroma is a soft, skin-colored tender growth that looks like a mole or skin tag and forms along the pathway of a nerve. They are commonly seen in children entering puberty, pregnant women, and older adults.
Sebaceous Hyperplasia
These small white or yellow growths appear as small domes on the skin with an indentation in the center of the dome. They are formed due to enlarged or clogged oil glands in the skin.
Seborrheic keratosis

Seborrheic Keratoses are common and numerous in older adults. These growths are tan to black in color and have a dry, wart-like, smooth or flat appearance Dermatosis papulose nigra appear as small black bumps around the eyes and on the cheeks.
Skin Tag
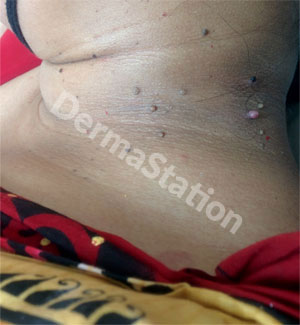
Skin tags are small, skin-colored growth sticking out from the skin. Common sites are the neck, trunk, armpits, or in or near skin folds. They are more common in people who are obese or diabetic, and in pregnant women.
How are common Growths Treated?
Most common skin growths do not require treatment. Growths can be removed if they become irritated, painful, or inflamed (red and swollen) or just for cosmetic reasons.

Eczema is a skin disease characterized by patches of dry or red, itchy skin. Scratching the skin damages its surface and can worsen the rash. A person is more likely to get eczema if a parent or family member has eczema, asthma, or hay fever. Genes and environment play a role in causing eczema. Living in an urban area and / or living in a cold or dry climate increases the risk of having eczema.
The skin looks inflamed and sore. Patches of eczema can crack, leak clear fluid, and crust. Repeatedly scratching and rubbing the patches can cause the skin to look pigmented and feel leathery

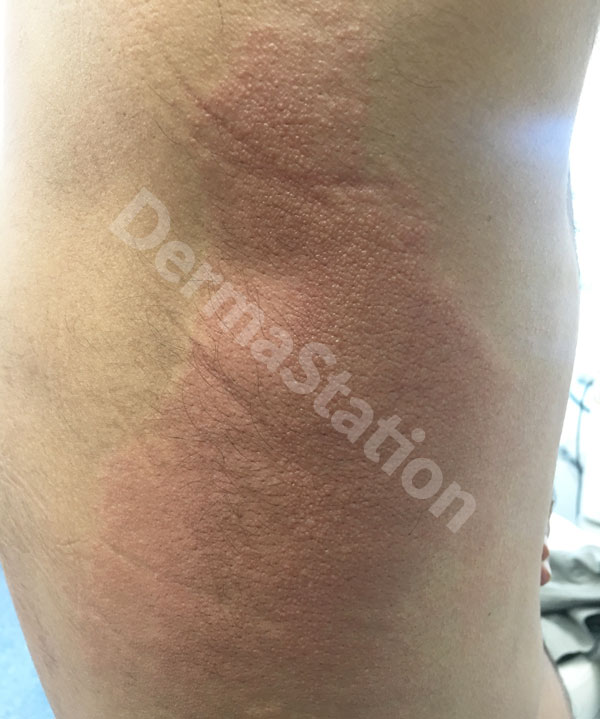
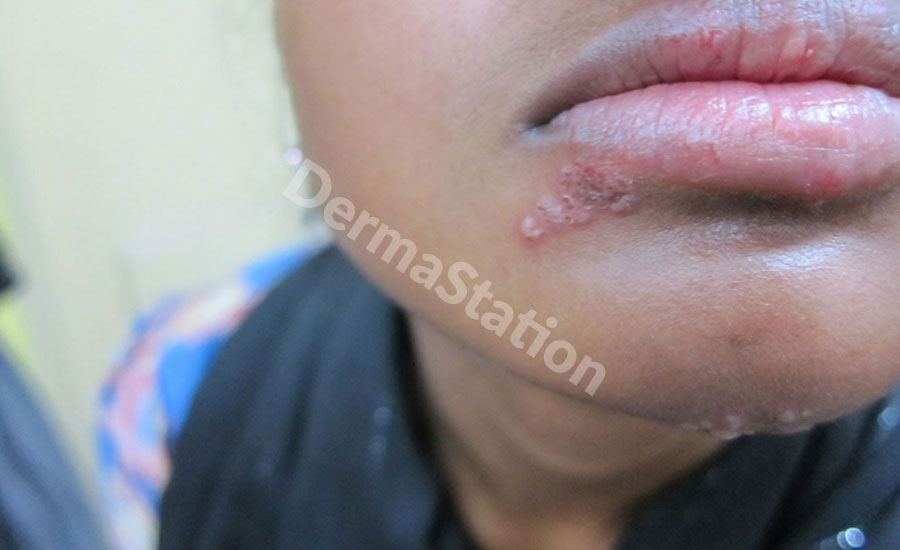
The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes blisters and sores around the mouth, nose, genitals, and buttocks, and almost anywhere on the skin. HSV sores are very annoying as they may reappear periodically, are painful and unsightly. There are two types of HSV – Type 1 and Type 2.
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
HSV Type 1 infections are tiny, clear, fluid-filled blisters that most often occur on the face, often referred to as cold sores or fever blisters. Type 1 may also develop in wounds on the skin.
Recurrent episodes can be triggered by a variety of factors including sun exposure, fever, menstruation, trauma (including surgery), or sometimes nothing at all.
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2
HSV Type 2 results in sores on the penis, buttocks, vagina, or cervix.
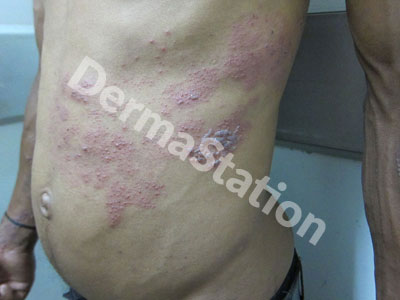
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles or zoster, is a viral infection caused by the same virus that cause chicken pox. Anyone who has had chicken pox can develop herpes zoster. The virus remains dormant (inactive), in certain nerve cells of the body, and when it reactivates it causes zoster. Illness, trauma, and stress or a temporary decrease in immunity (the body’s ability to fight infection) may trigger the virus to multiply and move along nerve fibers toward the skin. It is more common in people over the age 50.
Initially there may be burning, itching, tingling, or extreme sensitivity in an area limited to one side of the body before a rash appears at that site. The rash soon turns into groups of blisters which generally last for two to three weeks. Post-herpetic neuralgia is pain, numbness, itching, and tingling which may last long after the rash is clear.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) or acne inversa is a skin disease characterized by deep cysts in the armpits and groin where skin touches skin. It also involves areas under women’s breasts, on the buttocks, and around the anus. Females and people positive family history of HS have a higher risk of getting HS.
- Blackheads
- Pimple-like lesions that enlarge and become swollen, hot and painful
- Foul odor discharge
- Tunnel-like scar tracts under the skin
- Pain and difficulty in movement due to thick scars
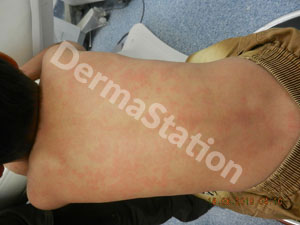
Hives (Urticaria) are erythematous itchy raised areas in the skin caused by a substance called histamine. They typically appear as pink or red swollen itchy spots of varying sizes on the skin. When hives occur after scratching or rubbing the skin, it is called dermatographism, which means “skin writing.”. 15-20% of people will get hives at some point in their lives. Infections are the most common cause of hives in young children. Other common causes of hives include medicines and foods. Less common causes include additives to foods such as preservatives and color dyes, stress, exercise, sunlight, and contact with cold substances like ice. In most cases, hives occur in perfectly healthy people.
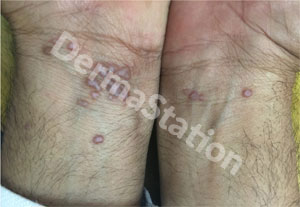
Skin
Lichen planus may present as few purplish raised lesions with fine, white, lacy-looking lines on them. Most common sites of involvement are the wrists, lower back, and ankles.
Mouth
Oral lichen planus can involve insides of the cheeks, gums, and tongue and appears as lacy white lines or raised white spots.
Nails
Nails affected by Lichen Planus lose their shine. Grooves and ridges appear on the surface of nails. They become thin and split.
Lupus can affect many organs in your body including skin.
| TYPE OF LUPUS | SKIN RASHES |
|---|---|
| Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) | Red, coin-shaped, and scaly patches, most often on the face scalp, and in the ears. Patches can remain on the skin for a long time, and usually heal with scarring |
| Subacute cutaneous lupus | Red, scaly patches, which usually forms on arms, shoulders

|
| Erythematosus (SCLE) | neck and trunk-photoexpsoed sites. Sometimes the rash can resemble psoriasis. |
| Acute cutaneous lupus | “butterfly rash.” across the nose and cheeks-looks like sunburn |
| Erythematosus (SCLE) |
Melasma is a condition characterized by skin discoloration that appears as dark, irregular-shaped patches with well- defined edges. Upper cheeks, nose, lips, upper lip, forearms, neck, and forehead are the common sites affected by it. Sun exposure trigger is a triggering factor for melasma as ultraviolet (UV)light from the sun stimulates the melanocytes, so it usually worsens during summer and improves during winter.
Melasma most often occurs in women especially pregnant women (chloasma or “the mask of pregnancy”) and those taking oral contraceptives triggred by hormones. Only 10-20 % of melisma patients are men. The main risk factors in men are sun exposure and a family history of melasma.
Melasma occurs when the color- making cells in the skin (melanocytes) produce too much pigment (color). Contributing factors include
Family history
- Pregnancy/lactation and use of birth control pills
- Facial and hair Cosmetics
- Phototoxic drugs (medicines that make the skin more susceptible to light damage,
- Sun exposure
- Stress
- Thyroid problems
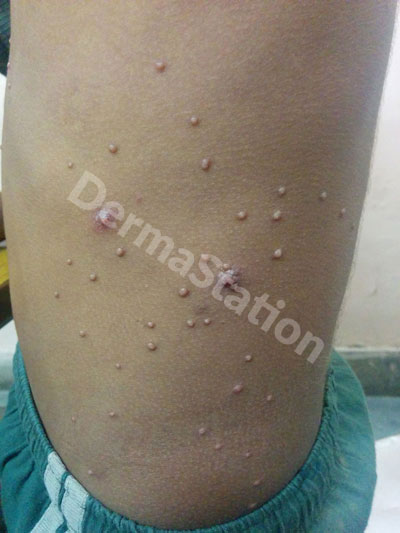
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection seen most commonly in young to school-age children caused by Molluscum Contagiosum Virus(MCV). It typically causes small, flesh-colored to pink bumps with a shiny appearance and slightly depressed center, which can occur anywhere on the body. The virus is contagious and spread by direct contact with the skin of an infected person or sharing personal items with someone who has molluscum.



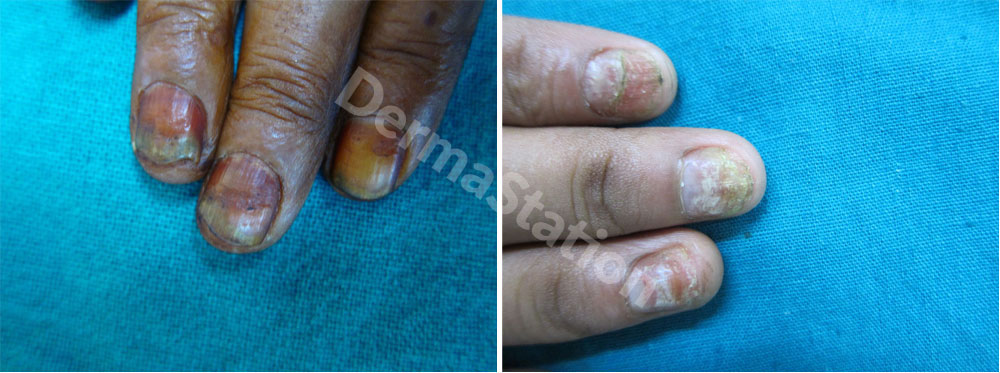
Nail diseases and warning signs of other internal health problems appear on the nails.
Nail Diseases
- Psoriatic nails: pits, ridges, and nail discoloration are the common signs of psoriatic nail involvement. The nails can separate from the nail bed, crumble, and split and the skin beneath the nail can turn reddish brown
- Fungal nail infection: When a nail thickens, splits, discolors, and lifts from the nail bed, fungal nail infection could be the cause.
- Bacterial nail infection:
- Ingrown nail: when the corner of a nail curves downward into the skin causing pain, swelling and discharge, most common on the big toe.
- Injured nail: small white spots often mean a nail injury
| Systemic Condition | Nail Appearance |
|---|---|
| Kidney disease | Half pink, half white nails |
| Liver disease | White nails |
| Diabetes | Yellowish nails with slight blush at base |
| Anemia | Pale nail bed |
| Heart condition | Red nail bed |
| Lung disease | Nails yellowing, thickening, growing slowly |
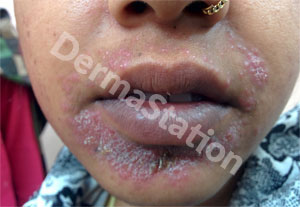
Perioral refers to the area around the mouth, and dermatitis indicates redness with itching on the skin. Along with redness, there may be small red bumps, and mild peeling. The area’s involved are within the borders of the lines from the nose, to the sides of the lips, and the chin. frequent sparing of a small band of skin that borders the lips may be seen. Perioral dermatitis mostly affects young women. If left untreated, perioral dermatitis may last for months to year. Strong corticosteroid creams applied to the face are the most common cause of perioral dermatitis.
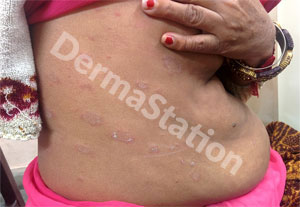
WHAT IS PITYRIASIS ROSEA?
Pityriasis rosea is a harmless rash, but it can be itchy. Pityriasis rosea tends to develop gradually. Many people initially develop one oval patch on their skin, Followed by all over body. It may be associated with sore throat, nausea, mild fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
What is pruritus?
The medical word for itch is Pruritus, a sensation that provokes the desire to scratch. Severe itching can be a significant source of discomfort and frustration for patient, and can lead to loss of sleep, anxiety, and depression. Pruritus can be a symptom of certain skin conditions, and sometimes a manifestation of an internal disease. When there is no evidence of skin or internal disease, pruritus may also be due to faulty processing of the itch sensation within the nervous system. The exact cause of an itch may remain unknown as it is a complex process.

Psoriasis is a common chronic skin condition in which red plaques with thick scales form on the skin. It affects 1-2% of all people and can develop at any age from infancy to adulthood. Psoriasis usually appears as dry, red, scaly patches on the skin which can itch and sometimes burn.
Immune system and genetics play major roles in the development of psoriasis. Psoriasis tends to run in families. Injury to the skin and infections are common triggers that bring out psoriasis or make it worse. Psoriasis is not contagious.
Plaque psoriasis commonly affect the elbows, knees and scalp. Psoriasis can also develop in the nails (usually in the form of small depressions or pits in the nail), and in the joints (called psoriatic arthritis). The severity of psoriasis can range from mild to severe and varies from person to person and may change over time.
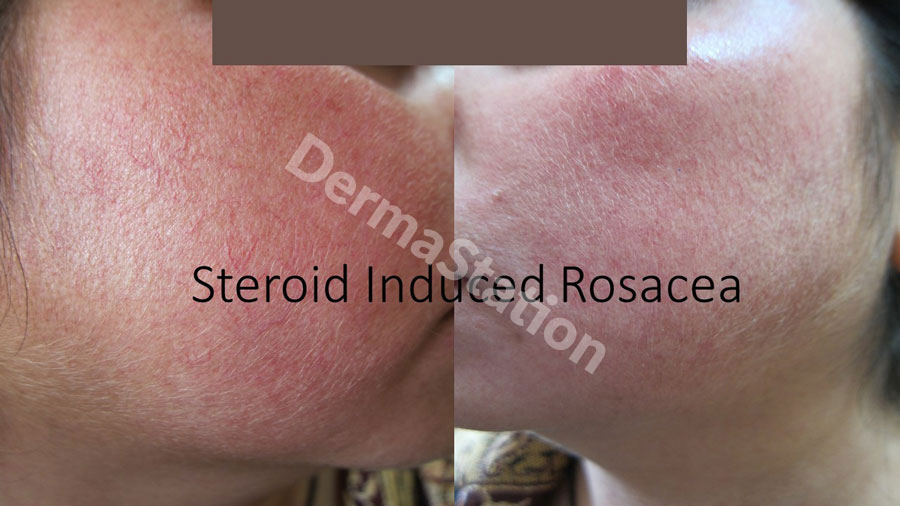
Rosacea is a common skin disease that causes persistent redness and swelling on the face. Fair-skinned women between the ages of 30 and 50 most likely to develop rosacea. Often referred to as “adult acne,” rosacea may begin as a tendency to flush or blush easily, and progresses to persistent redness in central face that may gradually involve the cheeks, forehead, chin, and nose. As the disease progresses, small blood vessels and tiny pimples begin to appear on and around the reddened area; however, unlike acne, there are no comedones. The condition rarely reverses itself, may last for years and can become worse without treatment.

Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin disease that causes a red, scaly, itchy rash. Most often it occurs on the scalp, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, and middle of the chest. This skin problem is easily treated, but chronic and recurring. Sometimes people use the terms dandruff, seborrhea, and seborrheic dermatitis to mean the same thing. However, these 3 terms differ. Dandruff causes scaling on the scalp but not redness. With seborrhea, the skin oily, mainly on the scalp and face, but has no redness or scaling. People with seborrhea may later get seborrheic dermatitis, which causes both redness and scaling.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects people of all ages most often, though, in infant and older adults.
In infants, the condition appears on the scalp (“cradle cap”). This mostly clears without treatment between 8 and 12 months of age. It is not contagious. In teens and adults, it tends to come and go and can be life-long. Elderly adults are prone to getting seborrheic dermatitis because of the effects of aging on the skin.
The presence of a yeast(fungal)-like organism, excessive release of oil from the skin and immune system, all play a part in causing seborrheic dermatitis. Excess oil from the skin acts as food source for the yeast, which in turn causes inflammation (redness and swelling), irritation, scaling, and flaking.
About Palmer Hyperhidrosis
Perspiration is a normal body function that helps us maintain a standard body temperature. Hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating. Hyperhidrosis results when the nervous system becomes overactive, resulting in heavy perspiration, especially on the palms, soles and underarms.
People suffering from palmer hyperhidrosis are hesitant to shake hands with others and often withdraw from social situations for fear of embarrassment. They also may have problems at work with activities requiring dexterity, like using a computer keyboard.

Tinea is a fungal infection of the skin, hair or nails. These fungal infections are named for where they occur on the body. Some examples are:
-
Tinea capitis (scalp)
-
Tinea corporis (body)
-
Tinea cruris (groin) – “jock itch”
-
Tinea faciei (face)
-
Tinea pedis (feet) – “athlete’s foot”
-
Tinea unguium or onychomycosis (nail)
Tinea capitis (scalp):
The scalp may show flakes of skin resembling dandruff or patches of hair loss or broken hairs.
Tinea corporis, faciei, and cruris (body, face and groin):
The fungal infection in these areas looks like a red, scaly ring with clearing in the center, hence the name ’ringworm’.
Tinea pedis (“athlete’s foot”):
The skin is usually moist and flaky between the toes. sometimes there are red, scaly rings on dorsum of the toes and feet, as well as flaky skin on the bottom or side of the feet.
Onychomycosis (nail fungus):
The nails get thick and discolored, and there is a buildup of loose skin and scales under the affected nails, especially at the outer edge of the nails.

Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of yeast (fungal organism) on the skin. Heat and humidity are predisposing factors leading to overgrowth of yeast. Tinea versicolor appears as small, light-colored dry, scaly spots on the skin. Spots may be tan to pink or very faint and can combine to from patches of lighter (or darker) skin.
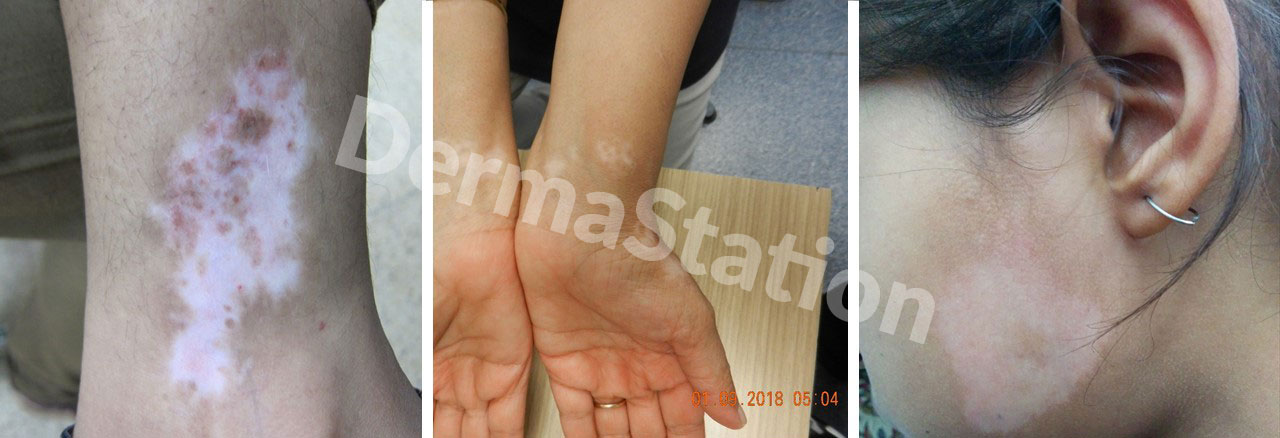
Vitiligo is a condition where individuals develop patches of white or lighter-colored skin.
Vitiligo is common, affecting up to 2% of the population worldwide. It is partially genetic and may run in families. It can affect all areas of the body, especially areas that are “bumped” or rubbed frequently (i.e., areas of friction like the elbows, hands, waist, knees and top of the feet).
Vitiligo results from destruction or reduction of melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in our skin, so that they cannot properly function. The cause of vitiligo is not clearly understood, but it appears in most cases to be an autoimmune condition where the body’s own immune system attacks the normal pigment-making cells in the skin.
For most people with vitiligo, white patches develop and expand slowly over time; however, every person is different. Some patients will never progress, rarely patients will worsen rapidly, and 10-20% will develop spontaneous repigmentation (return of normal color). A variant called segmental vitiligo is localized to a single strip of skin, and it is not usually associated with widespread loss of color.

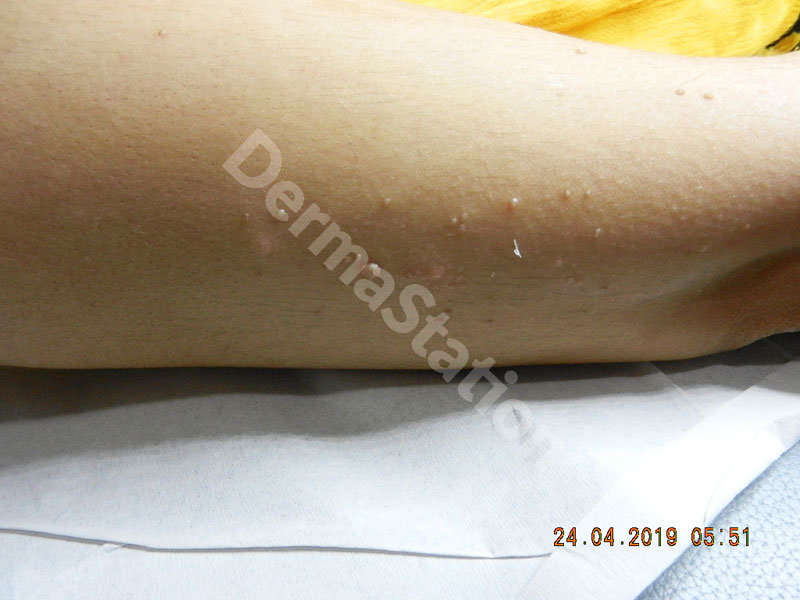
Warts are common viral infections caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV). Warts can go away without treatment as our own immune system learns how to fight them. About 60% of warts will disappear within about 2 years. There are many possible ways to treat warts and, sometimes, several different treatments are combined to get the warts to go away completely. There is no single perfect treatment for warts, and successful treatment can require multiple sessions. Read More >>

